As we venture further into the 21st century, the manner in which we approach healthcare continues to evolve. One of the most transformative advances has been telemedicine, where medical consultations are facilitated remotely using technology. The question remains: Is telemedicine the future of health consultation?
Understanding Telemedicine
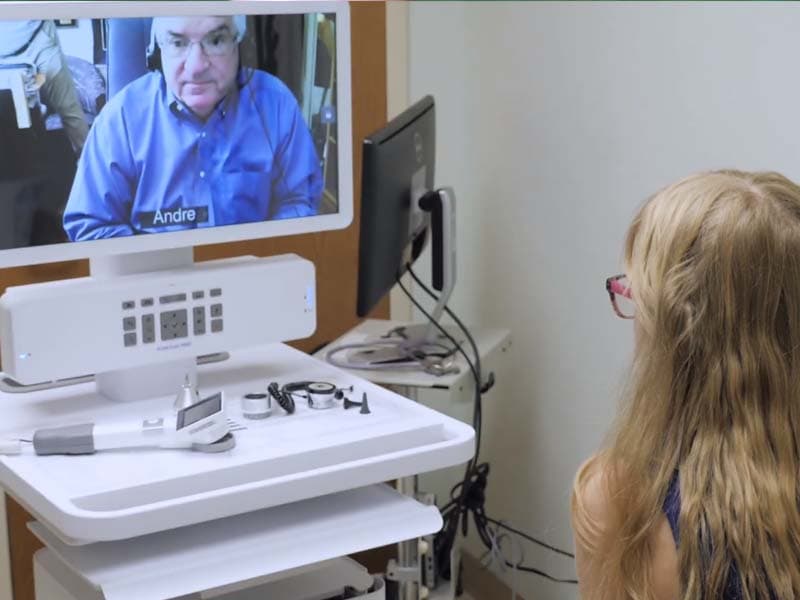
At its core, telemedicine refers to the practice of delivering medical care remotely, usually through video conferencing. It provides an interface between patients and medical professionals, allowing for consultations, diagnosis, and sometimes even treatment without the necessity for an in-person visit.
The Benefits
Accessibility: Telemedicine breaks down geographical barriers. People in remote areas or those who cannot travel easily now have access to quality healthcare.
Cost-Effectiveness: By reducing the need for physical infrastructure and in-person visits, there are potential savings for both medical professionals and patients.
Flexibility: Appointments can be more easily scheduled and rescheduled. This convenience factor is beneficial for both healthcare providers and patients.
Safety: In times of health crises, like the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine offers a safer alternative to in-person visits, minimizing exposure risks.
Continuity of Care: For chronic patients or those in ongoing treatment, it provides a seamless continuity of care without the necessity for frequent hospital visits.
The Challenges
Quality of Care: Physical examinations can be limited over a video call. Some conditions require tactile feedback or direct observation.
Regulations: Licensing and treatment regulations may differ between regions, making it challenging to offer telemedicine services across borders.
Data Security: Patient data must be transmitted and stored securely to maintain privacy.
Personal Connection: The physical presence of a doctor can be reassuring for many patients. Telemedicine may lack this human touch.
The Future: Integration Rather than Replacement
While telemedicine offers numerous advantages, it might not entirely replace traditional healthcare. Instead, the future is likely to see an integrated approach.
Hybrid Models: Patients could have initial consultations remotely, and based on the diagnosis, be called in for an in-person follow-up if necessary.
Expansion of Services: As technology advances, we can anticipate more diagnostic tools available for home use, further enhancing telemedicine’s potential.
Education and Awareness: As more people become familiar with the concept and advantages of telemedicine, its adoption will likely increase.
Policy and Regulation: As telemedicine becomes more prevalent, regulations will adapt to ensure quality of care and patient safety.
Can telemedicine diagnose?
Telemedicine has the capability to diagnose a wide range of conditions, but its scope and accuracy depend on several factors. Here’s a breakdown:
Type of Condition
Simple Ailments: Conditions like the common cold, flu, allergies, urinary tract infections, and minor rashes can often be diagnosed via telemedicine with a fair degree of accuracy.
Chronic Disease Management: For patients with known chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or depression, telemedicine can be useful for regular monitoring and adjustment of medications.
Specialized Consultations: Dermatology and psychiatry are two fields where telemedicine has been particularly effective. Visual examinations of skin conditions and psychological consultations can often be conducted effectively remotely.
Diagnostic Tools
Patient History: Many diagnoses in medicine are made by taking a thorough history, which can be done effectively via a telemedical platform.
Remote Monitoring Tools: With the advent of connected devices, patients can transmit real-time data to physicians. Devices like digital stethoscopes, blood pressure monitors, glucose meters, and pulse oximeters can provide valuable data remotely.
Images and Videos: For specialties like dermatology, high-quality images or video feeds can be sufficient for diagnosis.
Limitations
Physical Examination: Many conditions require a hands-on physical examination to diagnose accurately. For instance, palpating an abdomen, listening to lungs in multiple positions, or examining the movement of a joint might be essential for certain diagnoses.
Laboratory Tests: Many conditions require blood tests, urine tests, or other laboratory studies that cannot be performed remotely.
Advanced Imaging: Conditions that might need an X-ray, MRI, CT scan, or other imaging modalities cannot be fully diagnosed via telemedicine without those images.
Misdiagnosis Risks
While misdiagnosis is a risk in all forms of medical practice, the absence of a physical examination in telemedicine might elevate this risk for certain conditions. It’s crucial for healthcare providers to recognize the limits of telemedicine and refer patients for in-person evaluations when needed.
Integration with Traditional Medicine
The best telemedicine platforms integrate with traditional healthcare systems. For example, if a telemedicine doctor deems it necessary for a patient to get a lab test or an in-person examination, they can refer the patient to a local facility or practitioner.
Conclusion
While telemedicine may not completely replace traditional healthcare, it undeniably forms an essential part of the future of health consultation. Its growth and establishment signify a step forward in making healthcare more accessible, flexible, and in tune with the digital age. As we navigate the challenges and integrate telemedicine seamlessly into our healthcare models, we’re looking at a promising future that prioritizes patient well-being and convenience.